Diabetes Insulin Pump
Diabetes Insulin Pump
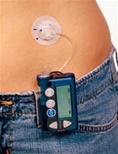
Insulin pumps provide an easy and effective way of delivering insulin to the bloodstream without having to inject using a needle. The pump is a small device, about the size of a pedometer, that you control to send the right amount of insulin into your system. You can set the pump to automatically and continually deliver minute amounts of insulin to your bloodstream to handle small rises of blood glucose. You also manually control the pump to deliver a larger amount of insulin (a bolus) after a meal or snack; or when your sugar level unexpectedly gets too high. This manual and automatic control simulates how a non-diabetic’s system controls their blood glucose levels.
The pump provides an excellent insulin delivery method for people with diabetes who need a constant supply of insulin or for diabetics who want to avoid injections. While the pump method still requires close blood sugar monitoring, it does eliminate the need to carry an insulin pen or syringe wherever you go.
If you need to remove the pump for a prolonged amount of time, you should be prepared to inject insulin using a pen or syringe, or, you can simply reconnect your pump for long enough to receive a dose of insulin.